 Daemar’s advice on technical considerations for choosing retaining rings
Daemar’s advice on technical considerations for choosing retaining rings
October 29, 2020 REDWIRE is news you can use from leading suppliers. Powered by FRASERS.
Posted by Daemar Inc.
Daemar manages the sourcing and delivery of millions of Essential Components to the manufacturing and MRO marketplace. I... Read more
Subscribe
Free REDWIRE e-newsletter
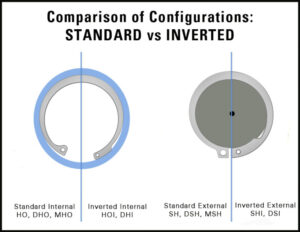
Daemar offers standard and inverted retaining rings.
Businesses want fasteners with economical designs that reduce weight, size, raw materials, and labour. Daemar Inc. supplies a wide range of retaining rings for different purposes. Choosing retaining rings is a process that should not be conducted hastily, since they are designed in various ways to work for different conditions.
A new blog entry by the Daemar team discusses the technical considerations that customers should weigh, to find the retaining rings right for their individual circumstances.
Properly cut ring grooves
In choosing retaining rings, the customer must note that they require properly cut grooves for optimal performance. Both groove ways should be parallel and perpendicular to the axis of the shaft or housing. Groove depth should be held to specifications, as the depth and bottom radii determine the amount of support the load-bearing groove wall provides. Reinforced retaining rings may be required to ensure the integrity of the application in some conditions, according to Daemar.
Another important criterion is basic versus inverted design, which depends on the loading conditions. When maximum groove engagement is required, basic rings are more appropriate, but when the lug protrusion of basic rings creates an interference problem, inverted rings are the better choice. Inverted rings are commonly used in low-load-capacity applications in which aesthetics are important.
For heavy loads, reinforced rings out-perform basic ones due to their greater section height, lug shape, and thickness. Reinforced rings are interchangeable with E-rings, for example, but they grip the groove bottom with far more radial force and offer more resistance to fatigue failure. Meanwhile, retaining rings can also be used to compensate for accumulated tolerances or wear in the assembly, or to exert pressure against the retained parts. Bowed rings can be flattened under pressure and return to their set heights when pressure is released.
Other options in choosing retaining rings include bevelled rings for rigid end-play take-up and self-locking rings on ungrooved shafts. The latter units are used on shafts without grooves, used widely for their relatively small outside diameters. Whatever the fastener requirement, there is a retaining ring that meets it.
To learn more, contact Daemar.
Share
Posted by Daemar Inc.
Daemar manages the sourcing and delivery of millions of Essential Components to the manufacturing and MRO marketplace. I... Read more
