 Contact plating material options for electronic connectors: Part 1
Contact plating material options for electronic connectors: Part 1
January 4, 2019 REDWIRE is news you can use from leading suppliers. Powered by FRASERS.
Posted by Harting Canada Inc
The family-owned HARTING Group is a global leader in connectivity solutions. HARTING invented the modular connector and... Read more
Subscribe
Free REDWIRE e-newsletter
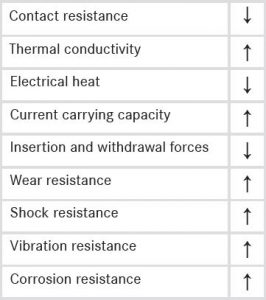
This chart shows the technical requirements for the contact zone of connectors.
In this six-part article, the HARTING Technology Group discusses plug-in connectors and options available for contact plating.
Plug-in connectors are used in a wide range of different environments and must perform reliably and consistently. Connector manufacturers must therefore focus on many aspects to ensure a good quality product. This includes consideration of the shape of the contacts, the number of contact points, the normal force, relaxation of the base material, and both the chemical composition and thickness of the plated contact surfaces. When choosing the right plating solution, connector manufacturers must pay careful attention to numerous technical requirements and physical demands. Until today, there have been many different contact surfaces for connectors available on the market. Every contact surface has its unique characteristics and its own advantages. This white paper will give a short overview over the contact system and common surface coatings used for electronic connectors. Furthermore, the focus is on a comparison between hard gold and hard gold flashed palladium-nickel (80/20), because in the field of data transmission via electronic connectors, these two coatings are the most common options used. Although this topic has been discussed earlier, there are still many questions. The respective characteristics and advantages of these two surfaces will be considered in more detail and confirmed by investigations done in the HARTING Quality & Technology Center.
Technical requirements for connectors
Plug-in connectors are used wherever components or assemblies have to be connected temporarily. The range of applications is as wide as the technical requirements for connector systems. Electrical contacts have basically two main tasks: the possibility to mechanical separate an electrical connection and the transmission of electrical energy without losses in closed position. To achieve this, the connector has to fulfill several technical requirements. The contact resistance should be low and, of course, stable; the thermal conductivity should be high so that the electrical heat is low and the current carrying capacity is high. The mating and un-mating forces should be low, and therefore, the connector should have a good wear characteristic. Likewise, it must be resistant to external influences like shock, vibration, humidity, and industrial atmosphere (corrosion resistance). These technical requirements and, therefore, the reliability of a connector system, is not only defined by the used contact surface; it is also influenced by several different physical properties, which depend on each other. The performance is defined, for instance, by the shape of the contact, the number of contact points, and the normal force, as well as the relaxation behavior of the base material. To facilitate the introduction to the subject of the contact surfaces, first, a brief overview of the structure of a connector, and more specifically of the contact zone, is given.
Coming up in Part 2: The contact system
To learn more, contact HARTING.
Share
Posted by Harting Canada Inc
The family-owned HARTING Group is a global leader in connectivity solutions. HARTING invented the modular connector and... Read more